
Rated gate drive voltage: When the gate drive voltage is within the range of ±20V and a voltage exceeding this range is applied, the oxide film (SiO2) between the gate and emitter may be insulated and damaged, resulting in reduced reliability.
VIEW MORE+
The lower IGBT needs to be turned on and off, and the upper IGBT is the same. The time interval between the two drive pulses needs to be adjusted to the calculated value of the dead time according to the actual situation. In this way, the negative current of the DC loop can be measured, and if the dead time is sufficient, no shoot-through current should be observed.
VIEW MORE+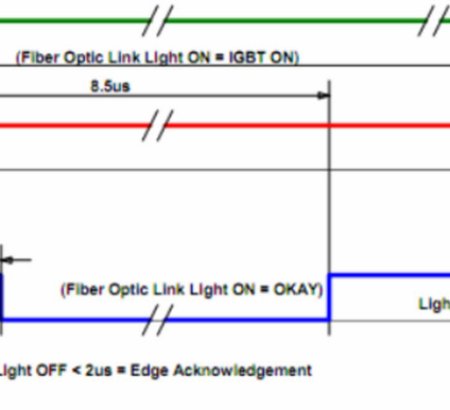
The shutdown sequence of the IGBT module three-level circuit when it fails In the three-level circuit with a 1-shaped diode clamp, when a short circuit fault or overcurrent fault occurs, the traditional way to shut down the IGBT is that the driver that detects the fault transmits the fault information to the controller, and then the controller shuts down the outer tube first, and then the inner tube. The reason for this specific shutdown sequence is: 1. If the inner tube is turned off first by mistake, the inner tube IGBT will bear the entire bus voltage, so the inner tube will be severely over-voltage and immediately damaged; 2. If the outer tube is turned off first, the voltage of the outer tube will be clamped at half the bus voltage, and there will be no overvoltage, and then the inner tube will be turned off, and the inner tube will be safe. The timing relationship of the traditional shutdown sequence when the three-level circuit fails:
VIEW MORE+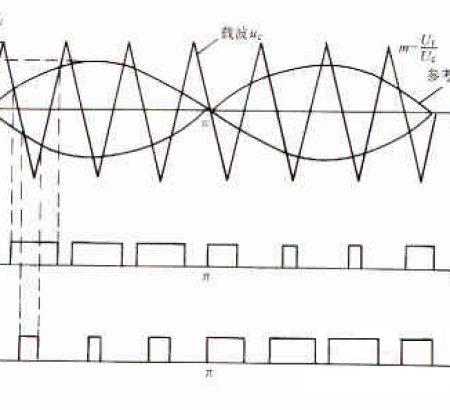
With the development of power devices, sine wave pulse width modulation (SPWM) technology has been widely used. SPWM control is to chop DC power into a pulse sequence with equal amplitude and width changing according to the sine law within one cycle of the inverter outputting AC power. The width of the pulse sequence is a discrete pulse that changes with the amplitude of the sine wave. After filtering, the sine wave AC power is obtained.
VIEW MORE+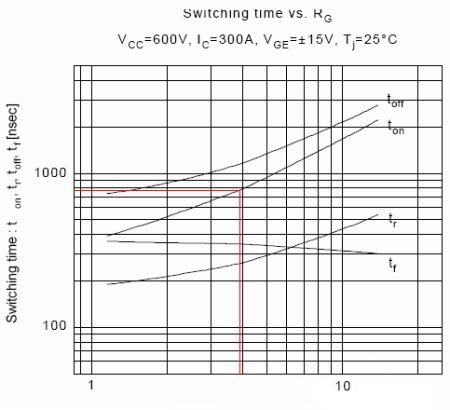
Regarding the design method of dead time, the formula TD'=TD-(t3+t4)+(t1+t2) is transformed to TD=TD'+(t3+t4)-(t1+t2)=TD'+(t3-t1)+(t4-t2). The rest is how to define the delay of the driver board (t1, t3) and the IGBT delay (t2, t4). The design method is divided into these two parts, the dead time of the IGBT part and the dead time of the HIC part. (1) Dead time of the IGBT part ① Collection of error data of IGBT switching time and calculation of maximum error data Based on the IGBT data of each company, calculate the error data of IGBT switching time (Tj=25℃). Based on σ and X±4σ, calculate X±4σ of each IGBT. (Maximum error) The following is the σ value of Fuji IGBT for reference. ○600V series σ=0.041 (maximum)
VIEW MORE+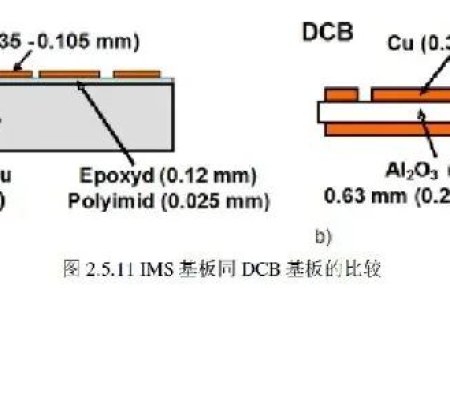
In electronic components (semiconductor modules), the material that separates the live parts from the base is called insulating material. In high-power semiconductor components, ceramic is often used as the base, which is a high-performance insulator.
VIEW MORE+